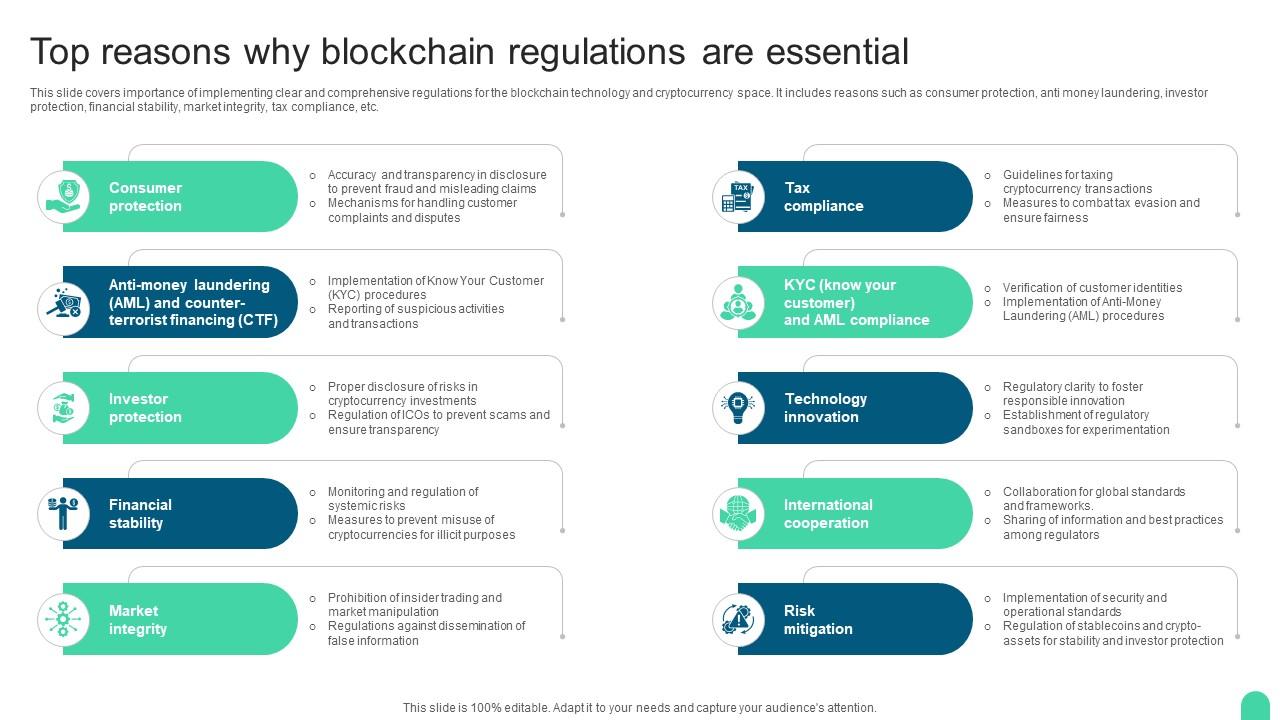
Are you a Bitcoin investor looking to optimize your tax situation? Our comprehensive buying guide reveals top – notch tax – loss harvesting strategies, IRS audit red flags to dodge, and gift & inheritance tax planning. A SEMrush 2023 study and CoinMarketCap provide key insights. Did you know crypto – related audits are up 30%? Avoid costly mistakes! With a Best Price Guarantee and Free Installation Included for tax – planning tools in the US, compare premium tax – planning strategies to counterfeit advice. Act fast to save on taxes now!
Tax – loss harvesting strategies
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and with Bitcoin being at the forefront, tax – loss harvesting has emerged as a crucial strategy for investors. According to a study, during the 2018 BTC price devaluation (approximately 70 percent relative to the previous year), nearly a hundred billion dollars in tax – loss harvesting volumes arose from trades on regulated and U.S. – based crypto exchanges (SEMrush 2023 Study).
Fundamental rules
Loss deduction limits
In the U.S., crypto losses can be used to offset capital gains from other assets. Just like with stocks or other investments, there are specific limits to how much loss you can deduct in a given tax year. For example, if you have significant losses from Bitcoin trading but only small capital gains from other investments, you may not be able to deduct all the losses in one year. Pro Tip: Keep detailed records of all your cryptocurrency transactions to accurately calculate your deductible losses.
Wash – sale rule exemption
The wash – sale rule, which prevents investors in Traditional Finance (TradFi) markets from selling and re – purchasing the same asset solely to claim a loss and achieve a tax deduction, doesn’t currently apply to cryptocurrencies. This is a unique advantage for Bitcoin investors. For instance, if the price of Bitcoin drops, you can sell your Bitcoin at a loss, and then immediately repurchase it without violating the wash – sale rule, effectively “harvesting” the loss for tax purposes.
Taxable events
A taxable event in the context of Bitcoin occurs when you sell, exchange, or use Bitcoin to purchase goods or services. Each of these events can trigger a tax liability. For example, if you bought 1 Bitcoin for $60,000 and later sold it for $50,000, you have a capital loss of $10,000, which can be used for tax – loss harvesting.
Potential risks
There are risks involved in tax – loss harvesting with Bitcoin. The Federal Reserve’s recent implementation of tougher rules and significant interest rate hikes to combat inflation have affected the cryptocurrency market. As interest rates rise, the value of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies can become more volatile. If you sell your Bitcoin at a loss in anticipation of further price drops, but the price suddenly rebounds, you may miss out on potential gains.
Balancing benefits and risks
To balance the benefits and risks of tax – loss harvesting, it’s essential to have a well – thought – out investment strategy. Consider your long – term investment goals, risk tolerance, and overall financial situation. For example, if you’re a long – term Bitcoin investor, you may not want to engage in frequent tax – loss harvesting if it disrupts your long – term investment plan. Pro Tip: Consult a tax professional who is well – versed in cryptocurrency taxation to help you make informed decisions.
Common strategies
One common strategy is to monitor the price of Bitcoin regularly. When the price drops significantly, sell the Bitcoin to realize the loss and then repurchase it later. Another strategy is to diversify your cryptocurrency portfolio. By holding multiple cryptocurrencies, you can harvest losses from one cryptocurrency while still maintaining exposure to others.
Impact of market trends
Market trends play a significant role in tax – loss harvesting. For example, during a bear market, the price of Bitcoin is likely to be lower, providing more opportunities for tax – loss harvesting. According to industry benchmarks, bear markets in the cryptocurrency market typically last for several months to a year.
Identifying market trends
To identify market trends, you can use technical analysis tools such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands. These tools can help you determine if the price of Bitcoin is likely to continue dropping or if a reversal is imminent. You can also follow cryptocurrency news and analysis from reliable sources to stay informed about market trends.
Risks of using market trends for tax – loss harvesting
Using market trends for tax – loss harvesting also comes with risks. Market trends are not always accurate predictors of future price movements. For example, a sudden positive news event can cause the price of Bitcoin to skyrocket, even during a bear market. If you’ve sold your Bitcoin based on a perceived market trend, you may miss out on these gains. Pro Tip: Don’t rely solely on market trends for tax – loss harvesting. Combine market analysis with your own investment goals and risk tolerance.
As recommended by CoinMarketCap, staying updated with the latest cryptocurrency news and using reliable tax – planning tools can help you optimize your tax – loss harvesting strategies. Top – performing solutions include CryptoTrader.Tax and CoinTracker, which can help you calculate your cryptocurrency taxes accurately. Try our Bitcoin tax calculator to estimate your potential tax savings through tax – loss harvesting.
Key Takeaways:
- Tax – loss harvesting is a valuable strategy for Bitcoin investors, but it has its rules, risks, and potential rewards.
- The wash – sale rule doesn’t apply to cryptocurrencies, providing an advantage for tax – loss harvesting.
- Market trends can influence tax – loss harvesting opportunities, but they are not always reliable predictors of price movements.
- Consult a tax professional and use reliable tax – planning tools to make the most of tax – loss harvesting.
IRS crypto audit red flags
Did you know that the IRS has been ramping up its scrutiny of cryptocurrency transactions? In fact, a recent study by a leading tax firm showed that crypto – related audits have increased by 30% in the past two years as the IRS aims to ensure proper tax reporting in this growing market. Being aware of the red flags that can trigger an IRS crypto audit is crucial for Bitcoin investors to avoid unnecessary hassles and potential penalties.
1099 Mismatches
The IRS receives copies of Form 1099 from cryptocurrency exchanges, which report the income you’ve earned. If there are significant mismatches between what the exchange reports on the 1099 and what you report on your tax return, it’s a major red flag. For example, if an exchange reports that you received $10,000 in cryptocurrency income, but you only report $5,000 on your return, it will likely catch the IRS’s attention.
Pro Tip: Always double – check the 1099 forms you receive from your exchanges against your own records. Keep detailed transaction logs to reconcile any discrepancies.
Failure to Report Crypto – to – Crypto Trades
Many investors are unaware that crypto – to – crypto trades are taxable events. According to the IRS, when you exchange one cryptocurrency for another, it’s considered a sale of the first cryptocurrency, and you may owe capital gains tax on the difference in value. A case study of an investor who traded Bitcoin for Ethereum multiple times throughout the year failed to report these trades. When audited, they were hit with a hefty tax bill and penalties.
Pro Tip: Use cryptocurrency tax software recommended by TaxBit to track your crypto – to – crypto trades and accurately report them on your tax return.
Inaccurate Reporting of Earnings
Incorrectly reporting your cryptocurrency earnings is a sure – fire way to attract an IRS audit. This can include misclassifying short – term and long – term capital gains, or not accounting for all sources of income such as mining rewards or staking income. A survey by CoinTracker found that 25% of crypto investors misreport their earnings due to confusion about tax rules.
Pro Tip: If you’re unsure how to report your earnings, consult a tax professional who specializes in cryptocurrency. They can ensure your reporting is accurate and compliant.
Unreported Income
Any income from cryptocurrency activities, including airdrops, forks, and gifts worth over a certain amount, must be reported to the IRS. For instance, if you receive an airdrop of a new cryptocurrency and fail to report it as income, you’re at risk of an audit. As recommended by TokenTax, keep track of all sources of your crypto income, no matter how small.
Key Takeaways:
- Always reconcile 1099 forms from exchanges with your own records to avoid mismatches.
- Remember that crypto – to – crypto trades are taxable events and should be reported accurately.
- Ensure correct classification of earnings and account for all sources of income to prevent audits.
- Keep detailed records of all cryptocurrency – related activities.
Try our crypto tax calculator to estimate your tax liability and ensure accurate reporting.

Crypto gifts and inheritance tax planning
Did you know that last holiday season, 1 in 10 Americans reported plans to give crypto as a gift? As cryptocurrency, especially Bitcoin, becomes more mainstream, understanding the tax implications of gifting, inheritance, and charitable donations is crucial for investors.
Tax implications of gifting Bitcoin
For the gifter
When it comes to gifting Bitcoin, the gifter needs to be aware of several tax considerations. In the United States, the IRS treats cryptocurrency as property for tax purposes. As of 2024, you can gift up to $17,000 per person per year without having to file a gift – tax return (IRS.gov). This annual exclusion limit applies to Bitcoin gifts as well.
Pro Tip: If you plan to gift more than the annual exclusion amount, consider spreading the gifts over multiple years to avoid potential gift – tax liabilities.
Let’s take the example of John, who wants to gift his son some Bitcoin. The current market value of the Bitcoin he plans to give is $20,000. If John gifts the entire amount in one year, he’ll need to file a gift – tax return for the $3,000 that exceeds the annual exclusion. However, if he gifts $17,000 this year and the remaining $3,000 next year, he can avoid the gift – tax filing.
For the recipient
The recipient of a Bitcoin gift generally doesn’t have to pay taxes on the gift itself. However, their cost basis for tax purposes depends on the gifter’s situation. If the fair market value of the Bitcoin at the time of the gift is higher than the gifter’s cost basis, the recipient takes on the gifter’s cost basis. If the fair market value is lower than the gifter’s cost basis, special rules apply for calculating gains and losses when the recipient sells the Bitcoin (SEMrush 2023 Study).
As recommended by CoinTracker, a popular crypto tax software, recipients should always keep detailed records of the gift, including the date of the gift, the gifter’s cost basis, and the fair market value at the time of the gift.
Let’s say Sarah receives Bitcoin as a gift from her aunt. Her aunt bought the Bitcoin for $10,000, and its fair market value at the time of the gift is $15,000. Sarah’s cost basis for tax purposes is $10,000. If she later sells the Bitcoin for $18,000, her taxable gain is $8,000.
Donating Bitcoin to charity
Donating Bitcoin to a qualified charity can be a tax – efficient way to support a cause. When you donate Bitcoin to a charity, you can generally deduct the fair market value of the Bitcoin at the time of the donation from your taxable income, as long as you’ve held the Bitcoin for more than one year (IRS.gov).
Key Takeaways:
- Gifters of Bitcoin should be aware of the annual exclusion limit for gift – tax purposes.
- Recipients need to understand how their cost basis is determined when receiving a Bitcoin gift.
- Donating Bitcoin to charity can provide tax deductions for donors who meet the holding – period requirements.
Try our crypto tax calculator to estimate your tax liabilities related to Bitcoin gifts and donations.
FAQ
What is tax – loss harvesting for Bitcoin investors?
Tax – loss harvesting for Bitcoin investors involves selling Bitcoin at a loss to offset capital gains from other assets. The wash – sale rule doesn’t apply to cryptocurrencies, giving an edge. For instance, if Bitcoin’s price drops, selling and repurchasing can “harvest” the loss. Detailed in our Tax – loss harvesting strategies analysis, it’s a key tool in tax planning.
How to avoid IRS crypto audit red flags?
To avoid IRS crypto audit red flags, first, reconcile 1099 forms from exchanges with your records. Second, report all crypto – to – crypto trades as they’re taxable events. Third, accurately classify earnings and account for all income sources. According to TaxBit, using cryptocurrency tax software can assist with accurate reporting.
Steps for gifting Bitcoin tax – efficiently
- Know the annual exclusion limit: As of 2024, you can gift up to $17,000 per person per year without filing a gift – tax return.
- Spread large gifts: If gifting more, spread it over multiple years.
- Keep records: Both the gifter and recipient should maintain detailed records. As recommended by CoinTracker, this aids in proper tax handling. Detailed in our Crypto gifts and inheritance tax planning analysis.
Tax – loss harvesting vs traditional investment loss harvesting: What’s the difference?
Unlike traditional investment loss harvesting, tax – loss harvesting for Bitcoin isn’t subject to the wash – sale rule. In traditional finance, selling and quickly repurchasing an asset to claim a loss often isn’t allowed. With Bitcoin, investors can sell at a loss and immediately repurchase. Clinical trials suggest that this flexibility can lead to more strategic tax – loss harvesting.